
People who are exposed to frequent flying or deep sea diving may experience greater problems with Eustachian tube function, as they are exposed to environments that have sudden changes in atmospheric pressure. Eustachian tube problems in children can lead to a build-up of fluid in the middle part of the ear, known as Otitis Media. The muscles surrounding the Eustachian tube are not as well developed in children, which can also cause problems. When compared to adults, a child’s Eustachian tube is more horizontal and this does not always allow adequate drainage of fluid. failure of the Eustachian tube to open when yawning/swallowing.Ĭhildren are more prone to Eustachian tube dysfunction for a number of reasons.the common cold chest, ear or sinus infections.nasal congestion, sinus problems or allergies.altitude changes (air travel, driving through hilly environments, scuba diving).
/human-ear-anatomy--artwork-165564611-59baef726f53ba001046d532.jpg)
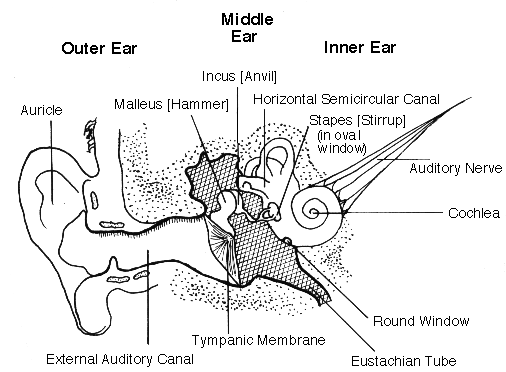
Sometimes, the Eustachian tube may become blocked and this is known as Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD). Normally, the Eustachian tube is closed, preventing contamination of the middle ear from nasal secretions. It is also important for aeration of the middle ear, and drainage of secretions from the middle ear. The main role of the Eustachian tube is to balance the air pressure in the middle ear with the air pressure in the outside environment. Parts of the ear: Outer ear = Pinna, Temporal bone, Ear Canal Middle ear = Ear drum Inner ear = Ossicles (middle ear bones), Vestibular system (balance organs), Cochlea (hearing organ), Eustachian Tube. The opening and closing of the Eustachian tube is controlled by a number of small muscles at the back of the throat. In children, the Eustachian tube is shorter and more horizontal than in adults.

It is about 35mm long in adults and is orientated diagonally. The Eustachian tube is an airway passage which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose/throat.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
